
Agriculture
May 27, 2024
DTW Lotus Biogas Burner
Read SolutionImplemented by
Development Technology Workshop

Updated on January 3, 2024
·Created on August 27, 2015
A chlorine dispenser to attach to flowing water systems.
The Lotus Water Project aims to reduce the transmission of water-borne diseases through the implementation of community-level water disinfection throughout urban slums. This chlorination device (currently a prototype) utilizes basic principles of fluid mechanics to dose water exiting a hand pump with the necessary amount of chlorine, making it safe to drink and store for later use. The chlorinator relies on pressure differences created by the device’s geometry to inject a dose of chlorine proportional to the amount of water flowing through the hand pump without using electricity (i.e. venturi effect). <sup> Interview with representative</sup>
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being
Market Suggested Retail Price
$0.25
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Community
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
As a prototype, Stanford Researchers and the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh are deploying the product. Lotus Water is developing a strategy for scaling its approach to water disinfection, one option being establishing an independent organization with full-time employees and a distribution network. Interview with representative
Countries
Bangladesh
Manufacturing/Building Method
The key parts are currently manufactured using 3D printers. All parts were purchased in Dhaka, Bangladesh with exception for the regulator and constant head tank. Interview with representative. Interview with representative
Intellectural Property Type
Open-source
User Provision Model
Landlords lease the device from Lotus Water company for the community’s water source. The landlord pays Lotus Water directly, and increases rent slightly to disperse the cost of the chlorination system evenly to each tenant; tenants pay the increased rent each month.
Distributions to Date Status
40 units
Active Chemical and concentration (%)
Sodium Hypochlorite (4%)
Form
Liquid
Dosing method: Batch or flow-through
Batch
Dosing method: Automatic or manual
Manual
Dosing quantity
0.4-0.6 mg/L
Contact time (min)
30
Target free disinfectant residual (mg/L)
Unknown
Bacteria reduction
Unknown
Virus reduction
Unknown
Protozoa reduction
Unknown
Heavy metals and/or arsenic reduction
Unknown
Treatment lifespan (days)
Unknown
Maximum recommended influent turbidity level (NTU)
Water should be low turbidity (<5 NTU) for best disinfection.
Design Specifications
The chlorinator is comprised of three core components—a venturi, a chlorine reservoir with a float valve (or constant-head tank), and a secondary chlorine reservoir. The venturi connects to the outflow of the hand pump and uses the venturi effect to draw in chlorine through an attached line.
Technical Support
During prototype phase, support is provided by field staff based at the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh; At maturity, Lotus Water Technicians will provide support. Interview with representative
Replacement Components
Not currently available for sale, but can be produced on a case-by-case basis. Interview with representative
Lifecycle
Technicians remove plastic chlorine bottles from each device site approximately once a month. The device is estimated to need full replacement every 2 years. Interview with representative
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Lotus Water provides water that is not only safe when it comes out of the tap, but is safe in storage because of the residual chlorine. Interview with representative
Vetted Performance Status
Field Testing ongoing. Within one three-month period, 1,100 samples were tested, of which 86% fell within WHO standards. Interview with representative
Safety
Plastic chlorine bottles to be removed from each device approximately once a month. The device is estimated to need full replacement every 2 years.
Complementary Technical Systems
Filtration prior to treatment can reduce the amount of chlorine needed, if source water is turbid.
Academic Research and References
Pickering, et al., Differences in Field Effectiveness and Adoption between a Novel Automated Chlorination System and Household Manual Chlorination of Drinking Water in Dhaka, Bangladesh: A Randomized Controlled Trial, PLoS One, 2015.
E. Action, “Using evidence to improve global well being,” Evidence Action, 01-Aug-2023. Available: https://www.evidenceaction.org/#dispensers
“Goal 6,” Sdgs.un.org. Available: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal6
“Cleaning Poop from Drinking Water,” KQED. Available: https://www.kqed.org/quest/74258/cleaning-poop-from-drinking-water
“Listing Category Search Page,” Nsf.org. Available: https://info.nsf.org/Certified/PwsChemicals/Listings.asp?CompanyName=&TradeName=&ChemicalName=Sodium+Hypochlorite&ProductFunction=&PlantState=&PlantCountry=&PlantRegion=
Compliance with regulations
NSF / ANSI Standard 60: Drinking Water Treatment Chemicals: Lotus Water is not specifically listed as complying, but dozens other companies selling sodium hypochlorite products for drinking water treatment are approved. This certifies that chemicals are safe at the maximum dose and that any impurities are below the maximum allowable limit.
US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Registration: Lotus Water is not registered with the EPA, sodium hypochlorite has been registered since 1957, and the EPA issued a registration standard in 1986 saying that sodium hypochlorite products (with 5.25% – 12.5% chlorine) do not need individual registration review. The document also states that, “widely used in disinfecting water supplies for nearly a century, the hypochlorites have been proven safe and practical to use.
World Health Organization (WHO):The World Health Organization does not currently approve products for use to treat drinking water. However, the Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality list liquid NaOCl with concentrations between 0.5% and 1% as a point-of-use water treatment method.
Evaluation methods
WHO recommendations for chlorine dosing and contact times; Randomized controlled trial to evaluate impacts planned for Dhaka, Bangladesh. Interview with representative
Other Information
Video on The Lotus Water Project. Please see Lotus Water's Gallery.

Agriculture
May 27, 2024
Implemented by
Development Technology Workshop

Agriculture
January 3, 2024
Implemented by
Suprio Das

Agriculture
January 3, 2024
Implemented by
Cascade Designers, Inc

Agriculture
February 20, 2024
Implemented by
Intellectual Ventures Lab

Agriculture
March 10, 2024
Implemented by
Disease Diagnostic Group

Agriculture
February 5, 2024
Implemented by
Circ MedTech
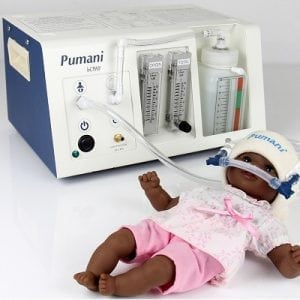
Agriculture
November 24, 2023
Implemented by
Hadleigh Health Technologies, and Rice 360
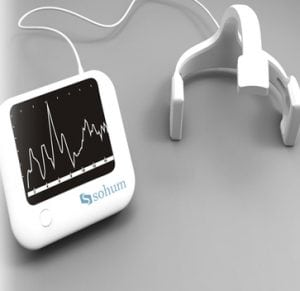
Agriculture
December 12, 2023
Implemented by
Sohum Innovation lab
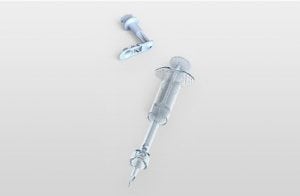
Agriculture
December 19, 2023
Implemented by
Star Syringe

Agriculture
September 26, 2024
Implemented by
Jorge Odón

Agriculture
May 27, 2024
Implemented by
Development Technology Workshop

Agriculture
January 3, 2024
Implemented by
Suprio Das

Agriculture
January 3, 2024
Implemented by
Cascade Designers, Inc

Agriculture
February 20, 2024
Implemented by
Intellectual Ventures Lab

Agriculture
March 10, 2024
Implemented by
Disease Diagnostic Group

Agriculture
February 5, 2024
Implemented by
Circ MedTech

Agriculture
November 24, 2023
Implemented by
Hadleigh Health Technologies, and Rice 360

Agriculture
December 12, 2023
Implemented by
Sohum Innovation lab

Agriculture
December 19, 2023
Implemented by
Star Syringe

Agriculture
September 26, 2024
Implemented by
Jorge Odón

Agriculture
May 27, 2024
Implemented by
Development Technology Workshop

Agriculture
January 3, 2024
Implemented by
Suprio Das

Agriculture
January 3, 2024
Implemented by
Cascade Designers, Inc

Agriculture
February 20, 2024
Implemented by
Intellectual Ventures Lab

Agriculture
March 10, 2024
Implemented by
Disease Diagnostic Group

Agriculture
February 5, 2024
Implemented by
Circ MedTech

Agriculture
November 24, 2023
Implemented by
Hadleigh Health Technologies, and Rice 360

Agriculture
December 12, 2023
Implemented by
Sohum Innovation lab

Agriculture
December 19, 2023
Implemented by
Star Syringe

Agriculture
September 26, 2024
Implemented by
Jorge Odón
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us FeedbackNotifications