
Agriculture
January 10, 2024
Oxfam Bucket
Read SolutionImplemented by
Oxfam

Updated on January 10, 2024
·Created on August 27, 2015
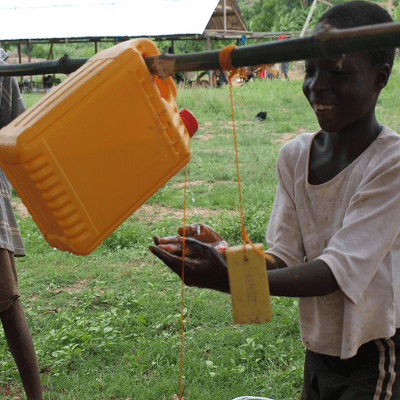
The TippyTap is a hands-free hand-washing station constructed using locally-available materials.
The TippyTap is a hands-free way to wash your hands appropriate for rural areas where there is no running water. It is operated by a foot lever and reduces the chance for bacteria transmission as the user only touches the soap. It uses only 40 mL of water to wash your hands versus 500 mL using a mug. Additionally, the used “waste” water can go to plants or back into the water table.
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Market Suggested Retail Price
$4.00
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Household, Community, Public Sector Agencies
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Anyone can access the online manual on how to make your own TippyTap.
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include EaziWash Station, PedalTap, and HappyTap.
Regions
Worldwide
Manufacturing/Building Method
The solution is individually made with local materials.
Intellectural Property Type
Open-source
User Provision Model
Any individual or organisation can build a TippyTap using locally available resources. There are numerous online resources and manuals available.
Distributions to Date Status
Unknown
Material
Wood, rope, water container, gravel
Activation mechanism
Foot pedal
Soap container built-in (yes/no)
Yes
Water volume per use (L)
40 mL
Design Specifications
The TippyTap is a simple device for hand-washing with running water. In general, the makeshift device 5 L container with a small hole near the cap, which is filled with water and tipped with a stick and rope. The device is operated by a foot lever, which reduces the chance for bacteria transmission as the user touches only the soap.
A gravel bed is used to soak away the water and prevent mosquitoes. When the container is empty, the cap is unscrewed and the container is removed from the stick. The container is then filled again at a water pump and reassembled for use.
Technical Support
Online manuals are available.
Replacement Components
Components can be replaced using locally available resources.
Lifecycle
Unknown
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Tippy Taps are designed to be simple and economical hand-washing stations, made with locally available materials and not dependent on a piped water supply.
Vetted Performance Status
This low-cost solution has been assessed and recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Foodborne and Diarrheal Disease Branch and Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. This is reflected in various publications released for public reference.
Safety
TippyTap is operated by a foot lever and thus reduces the chance for bacteria transmission as the user only interacts with the soap.
Complementary Technical Systems
None
Academic Research and References
Mbakaya, B.C., Kalembo, F.W., Zgambo, M., 2020, Use, adoption, and effectiveness of tippy-tap handwashing station in promoting hand hygiene practices in resource-limited settings: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 20 (1005).
Biran, A., 2011, Enabling Technologies for Handwashing with Soap: A Case Study on the Tippy-Tap in Uganda, Global Scaling Up Handwashing Project Working Paper.
Compliance with regulations
This solution is recommended by various organisations in expanding sanitation access in resource limited settings, particularly across Africa (e.g. World Bank's Water and Sanitation Program, Center for Disease Control).
Evaluation methods
This device is evaluated for its reduction in the incidence of diarrheal diseases, adaptability of the technology, amount of water used, and ease of use.
Other Information

Agriculture
January 10, 2024
Implemented by
Oxfam

Agriculture
January 9, 2024
Implemented by
PedalTap

Agriculture
January 10, 2024
Implemented by
Technology for Tomorrow (T4T) Africa

Agriculture
August 15, 2024
Implemented by
Biological Filters and Composters Ltd (Biofilcom)

Agriculture
January 3, 2024
Implemented by
Piramal Water Pvt Ltd.

Agriculture
January 17, 2024
Implemented by
Sanima

Agriculture
January 11, 2024
Implemented by
Centre for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technologies (CAWST)
Agriculture
January 10, 2024
Implemented by
Evenproducts

Agriculture
January 18, 2024
Implemented by
NextEra Distributed Water

Agriculture
December 29, 2023
Implemented by
Lifesaver
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback