
Agriculture
January 12, 2024

Updated on August 15, 2024
·Created on October 2, 2018
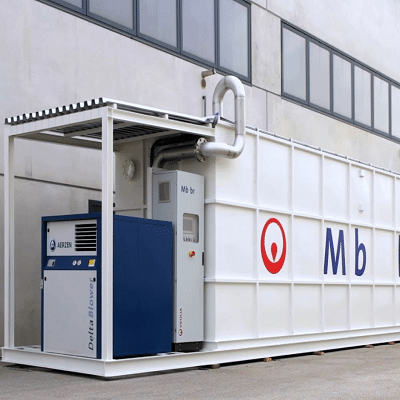
The AnoxKaldnes Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) is a wastewater treatment technology that consists of an aeration tank containing plastic media, on which biofilm can grow.
The AnoxKaldnes Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) is a wastewater treatment technology that uses biofilm carriers to optimize bacteria cultures for use in industrial and municipal applications. The plastic carriers are mixed with the wastewater by an aeration system, and the treated water flows out of the tank through a sieve. The compact system removes BOD, ammonia, and nitrogen, and the design of systems in flexible based on application.
The AnoxKaldnes MBBR is built and priced to bespoke configurations based on-site requirements.
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises, Public Sector Agencies
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Veolia Water Technologies UK
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include Sequential Batch Reactor, Membrane Biofilm Reactor, and Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems (DEWATS).
Regions
Worldwide
Manufacturing/Building Method
The AnoxKaldnes MBBR is built to bespoke configurations and customised to meet the sites specific requirements.
Intellectural Property Type
Patent
User Provision Model
MBBRs are designed with and then purchased though the manufacturer, to ensure that treatment is optimal for specific applications.
Distributions to Date Status
More than 600 MBBR systems have been implemented worldwide.
Flow rate (L/min)
100 – 800 L/min
Power Supply Type
Electrical
Technology type
MBBR, aeration, biofilm
BOD Removal Efficiency
96%
COD removal efficiency
99%
NH4-N Removal Efficiency
99%
TSS removal efficiency
85%
Total Phosphorus Removal Efficiency
68%
Fecal Coliform Removal Efficiency
100%
Design Specifications
The AnoxKaldnes MBBR system is designed as a tank with an inlet for wastewater and an outlet, covered by a sieve, for the treated wastewater. Small plastic biofilm carriers are mixed in the tank through aeration from the bottom of the tank. These carriers are designed to provide the optimal surface area for biofilm to grow on, effectively treating the wastewater.
Technical Support
Technical support is provided by the manufacturer through various water services and maintenance support packages. These packages include water plant maintenance and chemicals for water treatment. In addition all of the packages include remote technical support.
Replacement Components
Individual components are available from the manufacturer for replacement through the technical support plans.
Lifecycle
The AnoxKaldnes MBBR has has an observed operational lifespan of over 15 years with no reduction in performance.
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
The manufacturer specifies performance targets related to small plant footprints, accommodating high loading, and creating optimal bacteria culture conditions.
Vetted Performance Status
The product has been tested by a range of academic institutions including Lund University, Aarhus University, The University of Auckland, and the University of Ottawa related to design, functionality, and impact of temperature.
Safety
The AnoxKaldnes MBBR must be operated safely and correctly to ensure that users are not harmed by either the growing bacteria or the untreated wastewater.
Complementary Technical Systems
The system can be coupled with settlers, clarifiers, or disk filters which enable downstream separation of sludge from treated water.
Academic Research and References
McQuarrie, J., Boltz, J., 2011, Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor Technology: Process Applications, Design, and Performance, Water Environment Research 83: 560-75.
Hoang, V. et. al., 2014, Nitrifying moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) biofilm and biomass response to long term exposure to 1C, Water Research 49: 215-224.
Biswas, K., Taylor, M., Turner, S., 2013, Successional development of biofilms in moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) systems treating municipal wastewater, Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 98: 1429-1440.
Casas, M. et. al., 2015, Biodegradation of pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater by staged Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR), Water Research 83: 293-302.
Hoang, V., et al., 2014, An Investigation of Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor Nitrification during Long-Term Exposure to Cold Temperatures, Water Environment Research, 86: 36-42.
Biswas, K., Taylor, M. W., Turner, S. J., 2014, Successional development of biofilms in moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) systems treating municipal wastewater, Environmental Biotechnology 98: 1429-1440
Shokoohi, R. et al., 2017, Study of the efficiency of moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) in LAS Anionic Detergent removal from hospital wastewater: determination of removing model according to response surface methodology (RSM), Water Sci. Technology 2017(1): 1-7
Sidek, L. M., 2015, Experimental Comparison between Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) and Conventional Activated Sludge (CAS) for River Purification Treatment Plant, Advanced Materials Research 1113: 806-811
Hadei, M. et al., 2015, A survey on the performance of moving bed biofilm reactor and rapid sand filter in wastewater treatment, Journal of Advances in Environmental Health Research 3(3)
Piculell, M., 2016, New dimensions of moving bed biofilm carriers influence of biofilm thickness and control possibilities, Ph.D dissertation, Lund University, Lund, Sweden.
Zafarzadeh, A. et al., 2010, Performance of Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors for Biological Nitrogen Compounds Removal from Wastewater by Partial Nitrification-Denitrification Process, Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 7 (4): 353-364
Compliance with regulations
Veolia Water Technologies builds systems tailored to meet site objectives and to comply with regulations for applications such as water reuse, wastewater treatment and sewage treatment.
Evaluation methods
Each MBBR system is monitored and evaluated remotely during operation to ensure optimal system performance and to manage required maintenance.
Other Information
MBBR systems can be used in a variety of applications from wasterwater management to environmental protection. Here are the case studies related to two treatment projects:
Aquacria-Piscicolas Turbot Fish Farm
Patent Protected
This video further explains how the system works.
AnoxKaldnes MBBR Schematics

Agriculture
January 12, 2024

Agriculture
August 15, 2024
Implemented by
EAWAG
Agriculture
January 11, 2024
Agriculture
August 16, 2024

Agriculture
August 8, 2024
Implemented by
Patrick Kiruki, Banza Sanitation

Agriculture
January 10, 2024
Implemented by
Dr. David Manz, University of Calgary

Agriculture
August 13, 2024
Implemented by
The Africa Trust

Agriculture
August 14, 2024
Implemented by
Envirosan

Agriculture
August 14, 2024
Implemented by
WaterSHED

Agriculture
December 26, 2023
Implemented by
Mechanical Engineering Research & Development Organization (MERADO)
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback