
Agriculture
June 22, 2024
Lumeter PAYG Technology
Read SolutionImplemented by
Lumeter Networks

Updated on December 18, 2024
·Created on August 29, 2019
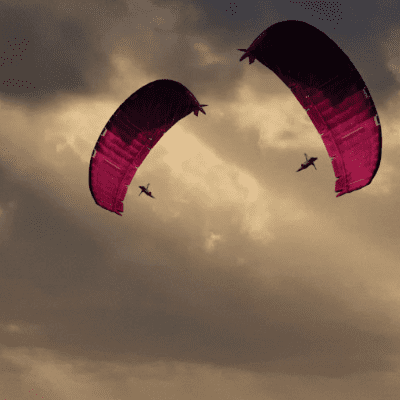
Kite Power Solutions uses two kites to access strong winds at high altitudes to generate power for off-grid, remote, offshore, or areas affected by natural disasters.
KPS (Kite Power Solutions) has the idea of generating electricity using kite technology. The kites are programmed to fly at high altitudes in a figure eight, accessing stronger wind speeds that generate lift for continuous energy generation. They aim to provide energy at a cost lower than conventional wind turbine energy, using 85% less material. Based on UK annual domestic energy usage, a KPS system can power 380 homes per year. The product is still in prototype phase.
Target SDGs
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Household
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
KPS aims to commercialize this technology by 2023. KPS plans to deploy its first 500 kW onshore power system at West Freugh, South West Scotland.
Manufacturing/Building Method
The system is being developed in Stranraer, South West Scotland.
Intellectural Property Type
Patent
User Provision Model
The product will be installed at specified locations to harness wind energy which will then be transmitted to the desired end-use sector.
Distributions to Date Status
KPS expects testing the kite in 2021 and the commercial deployment of the product by 2023.
Description of system
Kite
Start up windspeed (m/s)
Unknown
Power output, min (W at m/s)
Unknown
Power output, max (W at m/s)
500,000 W systems
Height of system (m)
Unknown
Radius of movement (m)
None
Description of control system
Unknown
Design Specifications
The system consists of two kites, with one of the two always generating power. The kites are programmed to fly in a figure eight pattern, accessing stronger wind speeds that generate lift. The tension induced results in a 100-200 m line spooled out from a drum on the ground, which is connected to a generator. While one kite is in the generation phase the other is in the retraction phase, to ensure continuous production of energy. In the generation phase, the tether is unreeled from a drum which produces electricity while the retraction phase reels in the tether of the kite.
Technical Support
Kites are reeled in and maintained at ground level. All components can be serviced at an accessible height.
Replacement Components
Unknown
Lifecycle
Unknown
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
The design aims to provide energy at a lower cost than a conventional wind turbine and use 85% less energy. KPS also aims to generate 15% more energy than a wind turbine at the same location.
Vetted Performance Status
Unknown
Safety
Potential hazards related to the operation of this product include the risk of bird collisions and an impact on the natural heritage of the region. The visual obstruction to the surrounding landscape must also be considered.
Complementary Technical Systems
None
Academic Research and References
These papers present general information about Kite Powered Systems:
Van der Vlugt, R., Peschel, J. and Schmehl R., 2013, Design and experimental characterization of a pumping kite power system, Ahrens, U., Diehl, M. and Schmehl, R., eds. Airborne Wind Energy Berlin: Springer.
Maass, J. and Erhard, M., 2013, Software system architecture for control of tethered kites, Ahrens, U., Diehl, M., Schmehl, R., eds. Airborne Wind Energy, Berlin: Springer, pp. 599–611.
Story. n.d. www.kps.energy.
Energy Investors Back Kite Power Company with £5m. 2016. www.imeche.org.
Compliance with regulations
Unknown
Evaluation methods
Unknown
Other Information
KPS predicts that the technology might not require government subsidies as the cost of energy from its offshore installments will be significantly lower than conventional offshore wind turbines.

Agriculture
June 22, 2024
Implemented by
Lumeter Networks

Agriculture
January 12, 2024
Implemented by
VIP
Agriculture
December 19, 2024
Implemented by
CLIMATENZA

Agriculture
June 10, 2024
Implemented by
Seameo Innotech
Agriculture
August 19, 2024
Implemented by
WERL Univesity of Toronto

Agriculture
September 18, 2024
Implemented by
Greenhouse Ventures
Agriculture
January 16, 2024
Implemented by
Emergy Enviro Pvt. Ltd

Agriculture
June 24, 2024
Implemented by
Angaza

Agriculture
December 7, 2024
Implemented by
Azuri Technologies

Agriculture
December 2, 2024
Implemented by
BioLite
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback