
Agriculture
June 3, 2024
CommCare
Read SolutionImplemented by
Dimagi
Updated on June 29, 2024
·Created on November 17, 2019
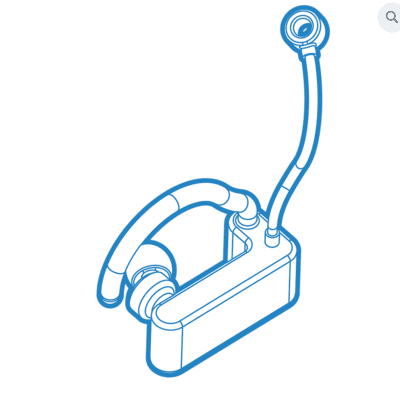
EXGbuds is a wearable device that allows users to control smart-home devices.
EXGbuds is a compact headset/earbud that generates actionable commands from simple eye movements and facial gestures. It allows users to interact with surrounding smart devices hands-free.
Target SDGs
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Household
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
EXG-wear
Regions
Worldwide
Manufacturing/Building Method
EXGbuds consists of customizable hardware and software, with biosensors placed on top of the ears combined with machine learning algorithms to measure various physiological signals to satisfy a variety of user needs.
The team developed their own patented Electroencephalogram (EEG) dry electrode sensors and microscale Bluetooth communication modules.
Intellectural Property Type
Trademark
User Provision Model
Directly from manufacturer
Distributions to Date Status
Unknown
Telecommunication service required (Y/N)
No
Communication protocol used
Bluetooth
Permanent network connectivity required (Y[specify]/N)
No
Type of data collected
Raw signals of eye and facial activities
Propietary hardware used (Y/N)
Yes
Sensors used (Y/N)
Yes, the device uses non-invasive biosensors
Open source code (Y/N)
No
Open source data (Y/N/ Other)
No
Operating system and version
Unknown
Power requirements
Unknown
Application
Assistive technologies, smart devices, virtual reality
Remote system diagnostics available (Y/N)
No
Design Specifications
By placing sensors and electronic modules in a compact and ergonomic way, EXGbuds provides a human-centered product design. Users can customize their own ergonomic design to place sensors at different locations to measure different physiological signals.
Technical Support
From manufacturer
Replacement Components
None
Lifecycle
Unknown
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Assist people with disabilities and improve productivity with augmented sensing.
Vetted Performance Status
The classification of the eye and facial gestures under the developed machine learning algorithm can reach to above 95% accuracy.
Safety
N/A
Complementary Technical Systems
None
Academic Research and References
Wang, K. J., Tung, H. W., Huang, Z., Thakur, P., Mao, Z. H. and You, M. X., 2018, EXGbuds: Universal Wearable Assistive Device for Disabled People to Interact with the Environment Seamlessly, Companion of the 2018 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, pp. 369-370.
Wang, K. J., Liu, Q., Zhao, Y., Zheng, C. Y., Vhasure, S., Liu, Q. and Mao, Z. H., 2018, Intelligent Wearable Virtual Reality (VR) Gaming Controller for People with Motor Disabilities, 2018 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality (AIVR), pp. 161-164.
Wang, K. J., You, K., Chen, F., Thakur, P., Urich, M., Vhasure, S. and Mao, Z. H., 2018, Development of Seamless Telepresence Robot Control Methods to Interact with the Environment Using Physiological Signals, in Companion of the 2018 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, pp. 44-44.
Wang, K. J., Zhang, A., You, K., Chen, F., Liu, Q., Liu, Y. and Mao, Z. H. , 2018, Ergonomic and Human-Centered Design of Wearable Gaming Controller Using Eye Movements and Facial Expressions, 2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), pp. 1-5.
Wang, K. J., Liu, Q., Vhasure, S., Liu, Q., Zheng, C. Y. and Thakur, P., 2018, EXG Wearable Human-Machine Interface for Natural Multimodal Interaction in VR Environment, Proceedings of the 24th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, p.49.
Home. (n.d.). EXG Wear. Retrieved June 29, 2024, from https://www.exg-wear.com
Modern Workplace. (n.d.). DXC Technology. Retrieved June 29, 2024, from https://dxc.com/us/en/offerings/modern-workplace
Goal 3. (n.d.). Sdgs.Un.Org. Retrieved June 29, 2024, from https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal3
Goal 9. (n.d.). Sdgs.Un.Org. Retrieved June 29, 2024, from https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal9
Shop. (n.d.). EXG Wear. Retrieved June 29, 2024, from https://www.exg-wear.com/shop
Wang, K.-J., Tung, H.-W., Huang, Z., Thakur, P., Mao, Z.-H., & You, M.-X. (2018). EXGbuds: Universal wearable assistive device for disabled people to interact with the environment seamlessly. Companion of the 2018 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, 369–370. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3173386.3177836
Compliance with regulations
Unknown
Evaluation methods
Academic research: several papers evaluated the accuracy of the machine learning algorithm that classifies human gestures into interaction with the device.
Other Information
None

Agriculture
June 3, 2024
Implemented by
Dimagi

Agriculture
June 22, 2024
Implemented by
Hospitainer

Agriculture
August 4, 2024
Implemented by
Partners for Development Taxi Service
Agriculture
June 12, 2024
Implemented by
Zipline

Agriculture
June 30, 2024
Implemented by
TUDelft

Agriculture
June 6, 2024
Implemented by
emocha Mobile Health

Agriculture
June 7, 2024
Implemented by
SES S.A.

Agriculture
June 8, 2024
Implemented by
Firas Rhaiem

Agriculture
June 2, 2024
Implemented by
RTI International

Agriculture
June 28, 2024
Implemented by
Swoop Aero
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback