Project Outcomes
Green Hydrogen (GH2) will play a crucial role in achieving India’s goals of energy independence by 2047 and net-zero emissions by 2070. GH2 is produced by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis, using electricity from renewable sources like solar and wind. It has the potential to decarbonize various sectors such as steel, cement, and transportation, which currently rely on fossil fuels and contribute significantly to India’s carbon emissions.
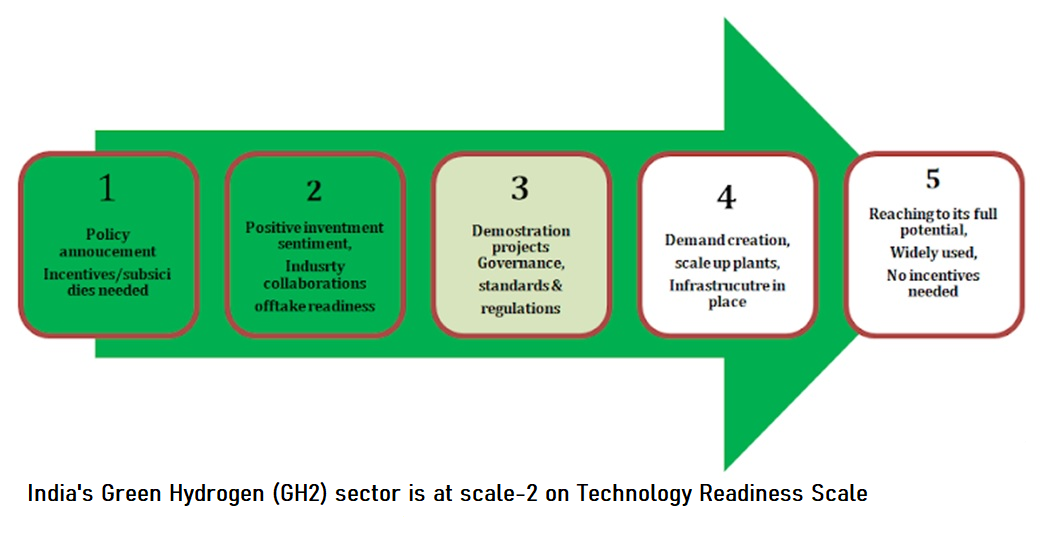
To support this transition, the Indian government launched the Green Hydrogen Mission-2023, targeting production of at least 5 million metric tons of GH2 by 2030, with a total outlay of INR 19,744 crore. This mission requires an additional 125 GW of renewable energy capacity and 60-100 GW of electrolyser capacity by 2030. The main objective of this project was to investigate the current state of GH2 value chain development in India and the technology readiness of Indian industries in areas such as electrolysers, storage vessels, processing equipment, and pipelines. The research outcome will play a crucial role in developing an action plan for ASME’s intervention to accelerate and support research. Extensive research was conducted to understand the GH2 value chain in India, identify stakeholders, and study the Green Hydrogen Mission-2023.
Survey forms were prepared for various stakeholders to gather information about technical, economic, and policy challenges facing GH2 industries in India, where the sector is in its nascent stage. The landscape analysis of data collected through desk research and surveys is documented in the report, informing AIPL and ASME to strategize their future initiatives and support in this space in India.
Shivaji Kale/ASME India Pvt. Ltd
