
Agriculture
June 26, 2024
A Tu Servicio Bogotá
Read SolutionImplemented by
Corona Foundation
Updated on December 1, 2023
·Created on June 17, 2014
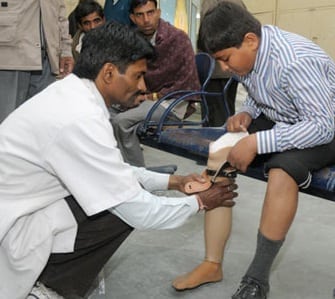
Jaipur foot provides different artificial limbs models, specializing in prosthetics for below-knee and above-knee amputees.
Jaipur Foot develops durable prosthetics for below-knee and above-knee amputees enabling sitting, running, squatting, climbing, walking and swimming.
Target SDGs
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being
Market Suggested Retail Price
$30.00
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Household, Community
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
BMVSS manufactures and distributes the Jaipur Foot in India. They reach other parts of India and other countries through temporary fitment camps (lasting a few days to several weeks) staffed by BMVSS employees. BMVSS has also established several associate organizations providing the Jaipur Foot in Pakistan and the Philippines and has also assisted with the creation of independent fitment centers throughout Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include ReMotion Knee V3.
Countries
Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India
Manufacturing/Building Method
Made by hand on an individual basis to the specifications of each beneficiary. BMVSS pioneered the use of a socket and shank fabrication using HDPE pipes, which simplifies the process to a single-step. The beneficiary is fitted for their prosthetic upon arrival at BMVSS and, generally, leaves the same day with their customized Jaipur Foot.
It has been noted that this process is cumbersome, involving laborious, repetitive, and non-standard techniques, resulting in product quality variability, low production volumes, and high reject rates. Further mechanization and streamlining of the manufacturing method are needed to standardize the production process.
Intellectural Property Type
Open-source
User Provision Model
About 20,000 limbs fitted a year by BMVSS (includes above-knee and below-knee prosthetics). Fittings take place at 22 permanent branches throughout India as well through 50 temporary fitment camps that take place yearly in various parts of India. Additionally, there have been 50 mobile clinics in 26 countries
Distributions to Date Status
513,806 limbs have been distributed as of March 2016.
Craftsmanship required
Skilled
Patient satisfaction
85%
Patient compliance
94%
Comfort
51%
Materials
High Density Polyethelene, Sponge rubber, wood
Water resistant (yes/no)
Yes
Amputation level
Transtibial
Weight (kg)
Unknown.
Design Specifications
Jaipur Foot is made of three blocks to simulate the anatomy of a human foot. The forefoot and heel blocks consist of sponge rubber, and the ankle block consists of light wood. They are bound together and enclosed in a rubber shell. A vulcanizer is then used to mold them into the shape of a foot. High-density polyethylene pipes are used to fabricate the socket and shank of the prosthetic. Open-ended and total contact sockets and exoskeletal and endoskeletal designs are fitted to the beneficiary as required. The size of the foot is variable based on the patient. Children need to have their prostheses adjusted every few months due to their rapid growth. All beneficiaries need adjustments and repairs to their feet over the course of several years due to normal wear and tear.
Technical Support
Little to no technical support required. Technicians are available at BMVSS facilities however to provide technical support if needed, such as making adjustments to the foot so it fits properly or making repairs after long term use of the foot. Also, BMVSS is known for the psychosocial support it offers beneficiaries during the fitting process. BMVSS also offers physiotherapy at its Jaipur headquarters.
Replacement Components
Beneficiaries are welcome to return to BMVSS facilities for continued assistance with repairs or replacements for their prosthetic
Lifecycle
Lifespan 2-5 years Disposal and Warranty not explicitly stated although it is mentioned that beneficiaries can return to BMVSS for adjustments or repairs (or a new foot in the case of children who have outgrown).
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Range of motion and durability that facilitates the activities Jaipur Foot was designed to accommodate Indian amputees (walking barefoot, working in wet fields, squatting, sitting cross-legged, walking on uneven ground, and climbing trees). The mechanical requirements are thus noted to be: dorsiflexion, transverse rotation, inversion, and eversion.
Vetted Performance Status
ISPO study found Jaipur foot to have a favorable durability record compared to other prosthetic feet tested in low-income countries, with 53% percent lasting longer than 3 years.
Safety
Ill-fitting prosthetic can result in physical discomfort and pain to the patient
Complementary Technical Systems
N/A
Academic Research and References
Jensen JS, Raab W. Clinical Field Testing of Vulcanized Jaipur Rubber Feet for Trans-Tibial Amputees in Low-Income Countries. Prosthetics and Orthotics International. 2006 Dec; 30(3):225-36.
Jensen JS, Craig JG, Mtalo LB, Zelaya CM. Clinical field follow-up of high density polyethylene (HDPE)-Jaipur prosthetic technology for trans-tibial amputees. Prosthetics and Orthotics International. 2004 Dec; 28(3):230-44.
Jensen JS, Treichl HB. Mechanical testing of prosthetic feet utilized in low-income countries according to ISO-10328 standard). Prosthetics and Orthotics International. 2007 Jun; 31(2):177-206.
Eaton D, Ayers S, Gonzalez RV. Comparison of Prosthetic Feet Roll-Over Shapes Used in Developing Nations. 5th World Congress of Biomechanics, Munich, Germany (2006).
Adalarasu K, Jagannath M, Mathur MK. Comparison on Jaipur, SACH and Madras Foot: A Psychophysiological Study. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Sciences and Technologies. 2011 4(1):187-192.
Arya AP, Lees A, Nirula HC, Klenerman L. A biomechanical comparison of the SACH, Seattle and Jaipur feet using ground reaction forces. Prosthetics and Orthotics International. 1995 Apr; 19(1):37-45.
Compliance with regulations
International Standards Organization (ISO) has a standards catalogue from their Prosthetics and Orthotics Technical Committee. These are not are referenced by BMVSS.
Evaluation methods
ISPO has published several evaluation studies. Methods include roll-over shape testing to compare prosthetic foot/ankle mechanisms regardless of design differences, center of pressure (COP) measurements to analyze foot/ankle mechanism, range of motion, Static Proof testing, Static Strength test, Cyclic test, patient satisfaction, and patient compliance.

Agriculture
June 26, 2024
Implemented by
Corona Foundation

Agriculture
February 21, 2024
Implemented by
Inteco

Agriculture
September 27, 2024
Implemented by
Birthing Kit Foundation

Agriculture
February 22, 2024
Implemented by
AyuSynk

Agriculture
January 15, 2024
Implemented by
London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM)
Agriculture
February 23, 2024
Implemented by
Duke University
Agriculture
March 8, 2024
Implemented by
Laerdal Global Health
Agriculture
March 8, 2024
Implemented by
Lean Med
Agriculture
February 26, 2024
Implemented by
Envo mask

Agriculture
June 14, 2024
Implemented by
Enabling the Future
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback