
Agriculture
January 8, 2024
ElectroChemical Arsenic Remediation (ECAR)
Read SolutionImplemented by
Gadgil Lab, University of California Berkeley
Updated on January 12, 2024
·Created on August 9, 2019
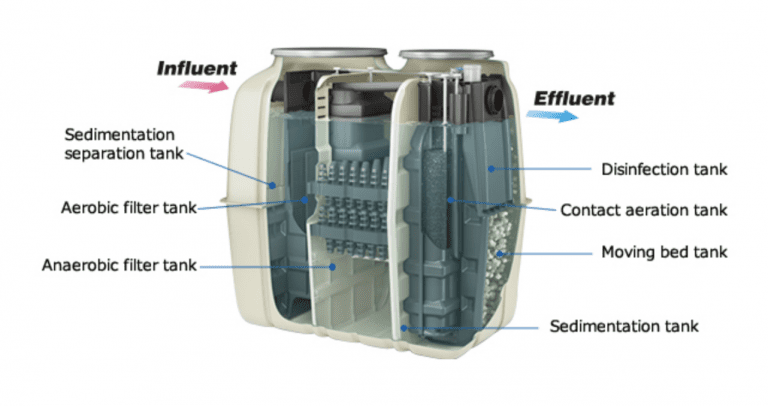
Johkasou tanks are wastewater treatment tanks that can be set up in areas without sewage infrastructure.
Johkasou tanks are commercialized wastewater treatment tanks that can be set up in areas without sewage infrastructure, combining both anaerobic and aerobic microorganisms. Steps include a solid-liquid separation tank, an anaerobic filter bed tank, a moving bed tank or membrane bioreactor, a carrier filter tank or sedimentation tank, followed by the disinfection tank. The product is designed and manufactured by Kubota in Japan, and distributed primarily in Asia.
Six different models exist: KZ II, HCZ, KM-SG-NP, K-HC-T, K-HC-R, KTZ
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Household, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises, Public Sector Agencies
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Unknown
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include AnoxKaldnes Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor, Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems (DEWATS), and The Biofil Digester.
Regions
Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia, South Asia
Manufacturing/Building Method
Manufactured in Japan for small, medium, and large application settings.
Intellectural Property Type
Patent
User Provision Model
Users can contact local sales information centers
Distributions to Date Status
1,000,000 units have been distributed in Japan, and an additional 1,000 distributed overseas
Flow rate (L/min)
Flow rate for different available models:
KZ II: 0.7-1.4 L/min
HCZ: 2.9-6.9 L/min
KM-SG-NP: 13.9-138.9 L/min
K-HC-T: 6.9-20.8 L/min
K-HC-R: 13.9-69.4 L/min
KTZ: 6.9 L/min
Power Supply Type
Electrical
Technology type
Solid-liquid separation tank, anaerobic filter bed tank, moving bed tank, membrane bioreactor, carrier filter tank, sedimentation tank
BOD Removal Efficiency
BOD, mg/L, for available different models:
KZ II: ?20
HCZ: ?20
KM-SG-NP: ?5
K-HC-T: ?20
K-HC-R: ?20
KTZ: ?20
COD removal efficiency
COD, mg/L, for available different models:
KM-SG-NP: ?10
KTZ: ?30
NH4-N Removal Efficiency
Total N, mg/L, for available different models:
KZ II: ?20
HCZ: ?20
KM-SG-NP: ?10
TSS removal efficiency
SS, mg/L, for available different models:
KZ II: ?15
HCZ: ?15
KTZ: ?15
Total Phosphorus Removal Efficiency
Total P, mg/L, for available different models:
KM-SG-NP: ?1
Fecal Coliform Removal Efficiency
Unknown
Design Specifications
Johkasou design specifications vary according to model.
Six products exist: KZ II, HCZ, KM-SG-NP, K-HC-T, K-HC-R, KTZ
Technical Support
Provided by Kubota
Replacement Components
Submerged membrane unit
Lifecycle
Unknown
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Manufacturer states product has 90% or higher BOD removal rate and delivers treated water quality with BOD of 20 mg/L or less (in case influent BOD is 200 mg/L).
Vetted Performance Status
Unknown
Safety
Blower must remain on for microorganisms (stopping will result in untreated wastewater and bad odor). Do not throw foreign objects (such as rubber, absorbent cotton, food wastewater, or cooking oil) in toilet to avoid clogging. Do not add chemicals (hydrochloric acid, insecticide, deodorant, chlorine agent, etc.) into the tank. Always close the manhole cover (and lock it if it has a locking mechanism). Prevent children from playing near the wastewater treatment plant. When closing a cover with bolt nuts, tighten cap nuts evenly using a special opening/closing handle. Be careful not to lose parts such as washers and gasket. Remove small stones and other foreign objects from the frame. Do not put any objects on the manhole, blower or power cable, or in the nearby area. Be sure to keep combustible or hazardous things away.
Complementary Technical Systems
Power source for blower
Academic Research and References
Ewiss, M.Z., Ahmed, Z.A., et al., 2017, Application Of The Japanese Johkasou Decentralized Sewage Wastewater System In Egypt, Sylwan 161(9): 180-193.
Gaulke, L.S., 2006, On-site wastewater treatment and reuses in Japan, Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Water Management 159: 103-109.
Lam, L. Kurisu, K. Hanaki, K., 2015, Comparative environmental impacts of source-separation systems for domestic wastewater management in rural China, Journal of Cleaner Production 104(1): 185-198.
Nguyen, L.H. Mohan, G. et al., 2016, Low-Carbon Watershed Management: Potential of Greenhouse Gas Reductions from Wastewater Treatment in Rural Vietnam, The Scientific World Journal.
Compliance with regulations
Unknown
Evaluation methods
Unknown

Agriculture
January 8, 2024
Implemented by
Gadgil Lab, University of California Berkeley

Agriculture
June 22, 2024
Implemented by
Hippo Roller

Agriculture
December 21, 2023
Implemented by
AID Foundation Inc. (AIDFI)
Agriculture
January 10, 2024
Implemented by
Ideas at Work

Agriculture
December 29, 2023
Implemented by
Lifesaver

Agriculture
January 16, 2024
Implemented by
Solvatten

Agriculture
January 20, 2024
Implemented by
Technology for Tomorrow (T4T) Africa

Agriculture
August 15, 2024
Implemented by
EAWAG

Agriculture
December 29, 2023
Implemented by
Tapp Global Design Inc

Agriculture
January 4, 2024
Implemented by
iDE
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback