
Agriculture
January 2, 2024
The TFP Composting Toilet
Read SolutionImplemented by
Toilets for People

Updated on January 17, 2024
·Created on September 26, 2019
The NADEP method of organic composting uses a wide range of organic materials such as crop residues, weeds, forest litter and kitchen waste with an end-product of a fertilizer that serves as a good alternative to farmyard manure.
The NADEP Composting method of organic composting was developed by a Narayan Deotao Pandharipande of Maharashtra. This compost uses a wide range of organic materials such as crop residues, weeds, forest litter and kitchen waste with an end-product of a fertilizer that serves as a good alternative to farmyard manure. The composting tank construction is a rectangular brick tank with a 90-120 day decomposition time.
This method is free, requires a brick tank which price can vary depending on location.
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Resources Centre for Sustainable Development
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include Rotary Drum Composting and Vermicomposting.
Regions
Worldwide
Countries
India
Manufacturing/Building Method
Constructed using locally available materials
Intellectural Property Type
Open-source
User Provision Model
Users can use the open source design documents and implement the NADEP composting method.
Distributions to Date Status
Unknown
Input requirement (volume and frequency)
Agricultural waste (Dry & green): 1350-1400 kgs; Cattle dung or biogas slurry: 98 – 100 kgs; Fine-sieved soil: 1675 kgs; Water: 1350-1400 liters.
2 feet additional added 1 time after 15-30 days per 90-120 days for full compost
Additives
Water, soil
Production capacity (kg output per kg input)
~907 kg compost output per 1350-1400 kg agricultural waste input
Production duration
90-120 days
Percentage of nutrient recovery
1.4% nitrogen, 0.8% phosphorous
Complementary treatment needed
None
Design Specifications
The recommended size of the tank is 10 ft length by 5 ft width by 3 ft height. All the four walls of the NADEP tank have 6 inch vents (created by removing every alternate brick after the height of 1ft. from bottom for aeration), and the tank may be constructed with mud mortar or cement. For good quality compost, the entire tank should be filled within 24 hours and not beyond 48 hours. Initial materials include agricultural waste (Dry & green): 1350-1400 kgs, cattle dung or biogas slurry: 98 – 100 kgs, fine-sieved soil: 1675 kgs, water: 1350-1400 liters.
These materials are added in layers:
After 15-30 days add 2-3 additional layers, and moisten every 6-15 days. Decomposition time is 90-120 days.
Technical Support
There is no technical support provided and users are expected to maintain the product on their own.
Replacement Components
None
Lifecycle
Unknown
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Reduced cash expenses on chemical fertilizer, improved soil fertility, and increased crop yield
Vetted Performance Status
Testing by S.V.P University assessed nutrient retention, S.K. Rajasthan Agricultural University assessed carbon loss, and additional testing for S.V.P. University assessed weed recycling through NADEP composting.
Safety
Implementers must take appropriate precautions when working with organic waste, particularly cattle dung, and ensure complete decomposition.
Complementary Technical Systems
None
Academic Research and References
Kumar, S., at al., 2011, A Study on Design and Development of NADEP Compost Tank, Society for Recent Development in Agriculture 11(1): 207-209.
Kumawat, N., et al., 2018, Preparation of NADEP Compost for Sustaining Farming Community. Popular Kheti 5(4): 56-60.
Kumar, A., et al., 2012, Recycling of Harmful Weeds Through NADEP Composting. VEGETOS: International Journal of Plant Research 25: 315-318.
Verma, R., et al., 2014, Carbon and Weight Loss During Composting of Wheat Straw by Different Methods, Annals of Biology 30 (2): 354-357.
Compliance with regulations
Unknown
Evaluation methods
Nutrient retention, decomposition of different organic materials, and carbon loss were all assessed in evaluations.
Other Information
Information about Resources Centre For Sustainable Development can be found here.

Agriculture
January 2, 2024
Implemented by
Toilets for People

Agriculture
August 13, 2024
Implemented by
Sun-Mar

Agriculture
December 18, 2023
Implemented by
Clivus Multrum
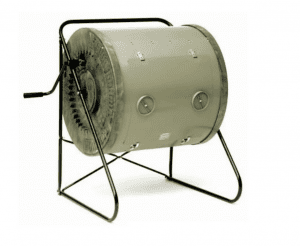
Agriculture
January 11, 2024

Agriculture
August 16, 2024
Implemented by
EcoSwell

Agriculture
January 11, 2024
Implemented by
Caminos de Agua

Agriculture
January 17, 2024
Implemented by
Aquagenx

Agriculture
September 23, 2023
Implemented by
Innovations for Poverty Action

Agriculture
January 2, 2024
Implemented by
Deep Springs International

Agriculture
August 4, 2024
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback