
Agriculture
August 15, 2024
Struvite Reactor Tank
Read SolutionImplemented by
EAWAG
Updated on January 12, 2024
·Created on October 1, 2020
The NG-SEPCLEAN is a decentralized sewage treating septic tank developed to provide safe sanitation through treated wastewater.
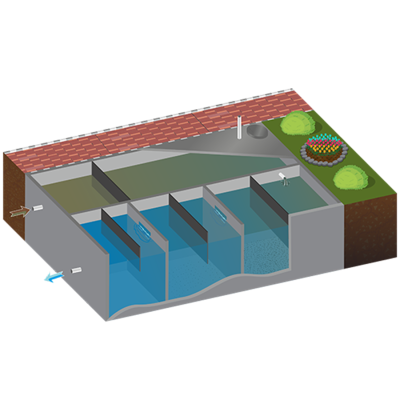
The NG-SEPCLEAN is a decentralized sewage treating septic tank developed to provide safe sanitation through treated wastewater, developed by Emergy Enviro Pvt. Ltd. The design is applicable where traditional septic tanks are unsuitable such as lack of space for a drain field, high water tables, proximity to wells or other bodies of water, and inadequate percolation. The NG-SEPCLEAN is designed for a high rate of digestion, low footprint, and reuse of treated wastewater.
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Household, Community, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises, Public Sector Agencies
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Emergy Enviro Pvt. Ltd, a SINE-IIT Bombay company
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include Johkasou, Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems (DEWATS), and The Biofil Digester.
Countries
India
Manufacturing/Building Method
Unknown
Intellectural Property Type
Trademark
User Provision Model
This product can be acquired by contacting Emergy Enviro Pvt. Ltd.
Distributions to Date Status
As of 2020, the NG-SEPCLEAN is implemented at 8 sites across India.
Flow rate (L/min)
Flow rate dependant on site specifications.
0.219-0.729 L/min (Households)
1.458-21.875 L/min (Public toilets)
Power Supply Type
No power required
Technology type
Sedimentation, Flocculation, Anaerobic, Aerobic, Filtration
BOD Removal Efficiency
70-80%
COD removal efficiency
75-85%
NH4-N Removal Efficiency
40-50%
TSS removal efficiency
75-90%
Total Phosphorus Removal Efficiency
30-35%
Fecal Coliform Removal Efficiency
80-90%
Design Specifications
The NG-SEPCLEAN requires less land space compared to traditional septic tanks. The principle components and functions include:
The system flow rate is dependant on the size and site specifications.
Technical Support
Provided by the manufacturer.
Replacement Components
Unknown
Lifecycle
30-40 years
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
The manufacturer specifies the following as performance targets:
Vetted Performance Status
The average removal efficiencies of the Decentralised Wastewater Treatment System (DEWATS) in Nepal is 96% TSS, 90% BOD5, 90% COD, 70% NH4–N, 26% TP and 98% FC.
Safety
Wastewater must be handled, treated and disposed of in accordance with hygiene and environmental standards.
Complementary Technical Systems
The effluent from these digesters can be further treated through Phytorid technology as a polishing step and then dispose into the river.
Academic Research and References
Singh, S., et al., 2009, “Performance of an anaerobic baffled reactor and hybrid constructed wetland treating high-strength wastewater in Nepal – A model for DEWATS“, Ecological Engineering 35: 654-660.
Kerstens, S. M., et al., 2012, “Evaluation of DEWATS in Java, Indonesia“, Journal of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene for Development 2: 254-265.
Reynaud, N., Buckley, C., 2015, “Field-data on parameters relevant for design, operation and monitoring of communal decentralized wastewater treatment systems (DEWATS)“, Water Practice and Technology 10: 787-798.
Compliance with regulations
Design and construction in compliance with IS 2470-2 (1985): Code of practice for installation of septic tanks, Part II: Secondary treatment and disposal of septic tank effluent.
Evaluation methods
The manufacturer cites solid and organic removal efficiency and 75-90% TSS removal evaluation criteria.
Other Information

Agriculture
August 15, 2024
Implemented by
EAWAG
Agriculture
February 4, 2024
Implemented by
Tank Connection

Agriculture
June 23, 2024
Implemented by
LoooP Creative Ltd

Agriculture
January 10, 2024
Implemented by
NRSRelief

Agriculture
January 22, 2024
Implemented by
Sanivation

Agriculture
December 13, 2023
Implemented by
change: Water

Agriculture
December 27, 2023
Implemented by
Nippon Basic Co. Ltd.

Agriculture
January 8, 2024
Implemented by
Gadgil Lab, University of California Berkeley

Agriculture
September 19, 2023
Implemented by
Grundfos

Agriculture
January 11, 2024
Implemented by
Precious Plastic
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback